Plastic vs Glass Fibers

Fiber Optics – data at the speed of light.
This week we’re talking about fiber optics, glass vs plastic, and the new DFS sensor lineup. Check it all out below and follow us on LinkedIn for the latest updates and future events and future developments!
Glass vs Plastic Fibers:
Plastic Optical Fibers can be easily misunderstood and consequently overlooked. Glass is better, right? Not always. Plastic fibers have a lot to offer. Here we will take a look at some of the interesting features of plastic fibers.
Plastic Optical Fibers are similar to glass fibers as they work the same way – they move the light from one end to another. But they are suited for use in different applications as well as made from different materials.
Both glass and plastic fibers will give a strong signal, but plastic fibers have several other benefits to consider. They are less expensive and have greater flexibility. They are resistant to bending, stretching, shock, and vibration.
Plastic optical fibers are also lighter in weight. They generally are sold with a cutting device that allows them to be trimmed to the desired length. They have excellent toughness and durability. They are waterproof, moisture-proof, and magnetic-free.
Compared to Glass fibers, Plastic fibers can really take a beating.
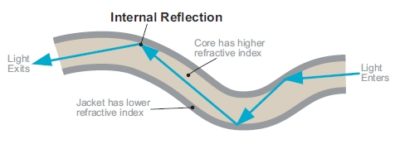
Bend Radius
The Bend Radius is the minimum radius a fiber can be bent without being damaged. The smaller the bend radius, the greater is the material flexibility. Most fibers can be bent up to 25mm (R25) without risk of damage, but the special High Flex fibers can be bent up to 10mm (or as specified).

Construction
Core – Thin plastic center of the fiber through which light travels.
Jacket – Layer around the plastic fiber to protect from damage and moisture.
Multi-core High-Flex plastic fiber differs from conventional plastic fibers in having multiple independent cores. This configuration allows a bending radius as small as 2mm. They can be bent with no reduction of light transmission. They can be threaded through machinery without the problems associated with extreme vibrations or pulling.

Coaxial – For Reflective Mode.
The center of the fiber core transmits; the ring of cores around the center is received. Received cores around the transmitted fiber core can receive the light from different directions thus increasing the accuracy of detection.
Connections
All fibers will fit a 2.2mm diameter fiber port on the sensor: either the plain cut end or with an adapter.

The DFS Sensor line:

Take a look at the newest line of digital fiber sensors. Designed to be easy to set up, provide real-time data, and deliver smart solutions.
