Reflective Encoder Technology

Advantages of Reflective Technology Encoders:
The primary component of the EPC reflective technology architecture is an innovative system-on-chip optical device. It combines a blue LED emitter and sensor into one package and also offers a variety of on-chip programmable encoder functions. This new reflective technology offers important advantages over the traditional optical transmissive approach used in encoders:
- A very compact design is possible because only a single PCB assembly is required instead of the two PCB assemblies needed when using transmissive technology.
- The short wavelength of the embedded blue LED improves signal contrast reducing jitter and the combined assembly of the emitter and sensor minimizes optical crosstalk. This allows for higher resolution, greater accuracy, and better performance.
- Most magnetic encoders utilize magnets located at the end of the encoder shaft to detect position. Reflective technology allows for off-axis position detection, allowing for more versatile mounting options including thru-bore style shafts.
Types of Reflective Encoder Technologies:
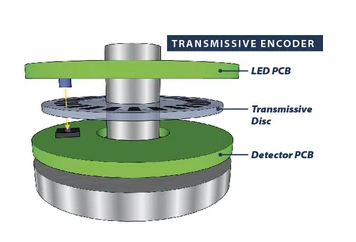 Transmissive Optical Encoders:
Transmissive Optical Encoders:
Most optical encoders are based on a transmissive optical architecture. This approach employs a high-quality LED light source that shines through a transmissive encoder disc and is received by a separate detector IC on the opposite side.
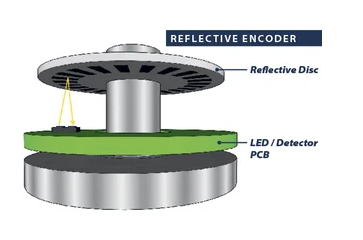 Reflective Optical Encoders:
Reflective Optical Encoders:
EPC’s newest encoder series utilizes reflective optical technology. In this approach, the LED and detector are located next to each other. The LED light shines onto a reflective disc and the reflected light waves are received by the adjacent sensor.
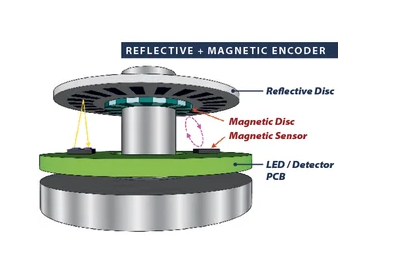 Reflective Encoders with Magnetic Sensing:
Reflective Encoders with Magnetic Sensing:
For absolute encoder applications that require a persistent multi-turn count, EPC offers an additional magnetic sensing option. The magnetic sensing system keeps track of the coarse multi-turn count in parallel with the optical sensor. However, the magnetic sensor is a special low-power device that can operate efficiently from an external power source when the primary power source is removed (a battery or controller with a UPS backup may be used). While operating from battery, the magnetic sensing system will remember the last multi-turn count value and track any additional turns that occur until primary power is restored.
